Detectability Analysis
Overview
Section titled “Overview”The detectability module provides tools for analyzing and visualizing source detectability data from lookup tables. It allows you to filter data, calculate detectability statistics, and create publication-quality heatmaps showing the fraction of sources detected at various delay times and observation times.
Key Features
Section titled “Key Features”- Flexible data loading: Works with Parquet or CSV files
- Custom column names: Supports any column naming convention
- Powerful filtering: Filter by any column using flexible operators
- Customizable visualization: Create heatmaps with full control over appearance
- Grid plotting: Compare multiple configurations side-by-side
Basic Usage
Section titled “Basic Usage”Loading Data
Section titled “Loading Data”The LookupData class is the main interface for working with detectability data:
from sensipy.detectability import LookupDatafrom sensipy.data.create_mock_lookup import create_mock_lookup_tablefrom pathlib import Pathimport tempfile
# Create a mock lookup table for demonstrationwith tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdir: lookup_path = create_mock_lookup_table( event_ids=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], sites=["north", "south"], zeniths=[20, 40, 60], delays=[10, 30, 100, 300, 1000, 3000, 10000], output_dir=tmpdir, )
# Load the data data = LookupData(lookup_path) print(f"Loaded {len(data)} rows")Filtering Data
Section titled “Filtering Data”Filter data by any column using flexible operators:
# Filter by site and zenithdata.set_filters( ("irf_site", "==", "north"), ("irf_zenith", "<", 40),)
# Filter by event IDsdata.set_filters(("event_id", "in", [1, 2, 3]))
# Multiple filters can be combineddata.set_filters( ("irf_site", "==", "south"), ("irf_zenith", "==", 20), ("event_id", ">=", 2),)Supported operators: ==, =, <, >, <=, >=, in, not in, notin
Creating Heatmaps
Section titled “Creating Heatmaps”Generate detectability heatmaps with customizable options:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Set observation times for the analysisdata.set_observation_times(np.logspace(1, np.log10(3600), 10, dtype=int))
# Create a basic heatmapfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 8))data.plot( ax=ax, title="Source Detectability: CTAO North, z20", max_exposure=1, # Maximum exposure time in hours return_ax=True,)plt.tight_layout()plt.savefig("detectability_plot.png", dpi=150, bbox_inches="tight")plt.close()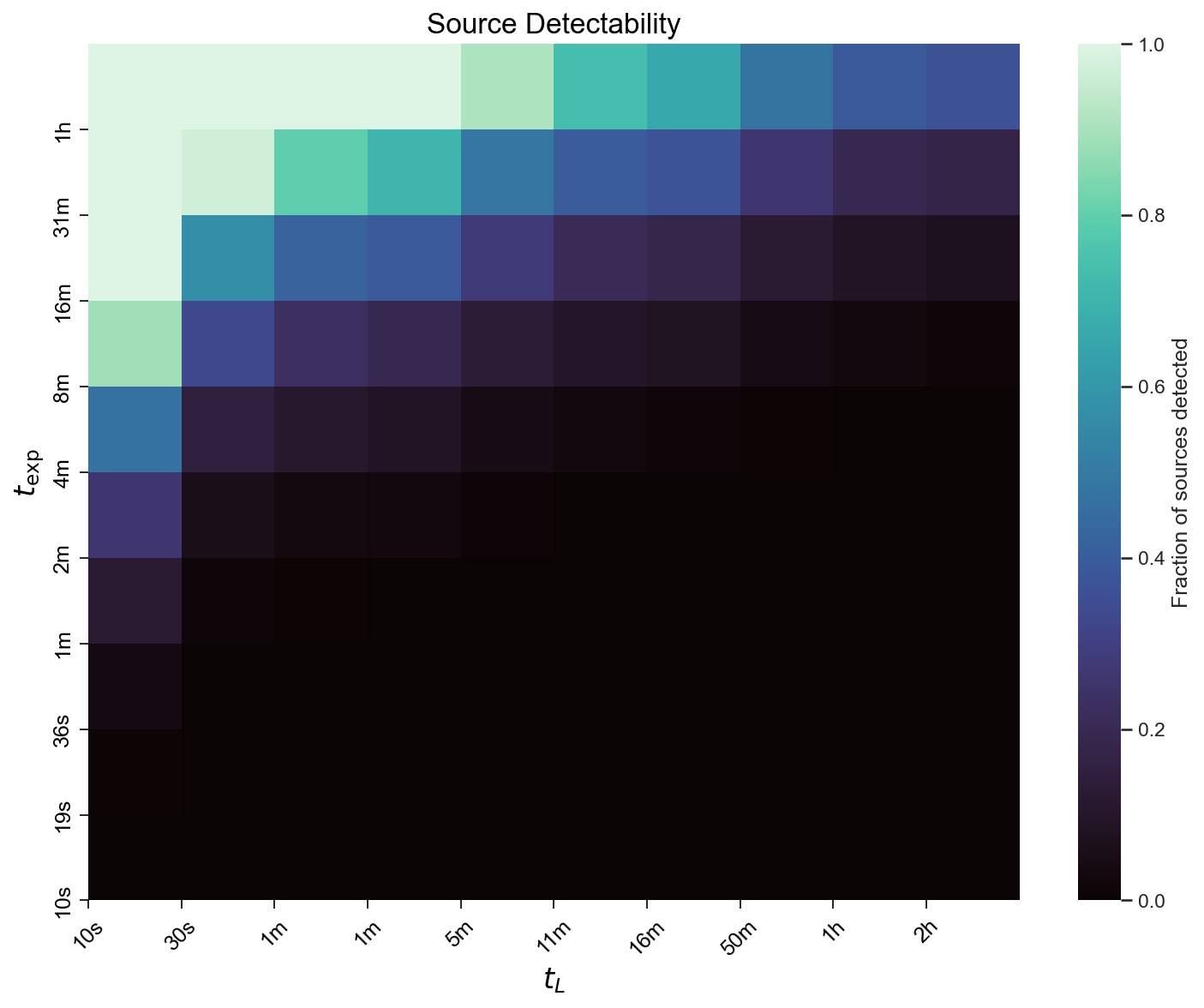
Customizing Plots
Section titled “Customizing Plots”The plot() method offers extensive customization options:
data.plot( ax=ax, title="Custom Detectability Plot", max_exposure=2, # Maximum exposure time in hours as_percent=True, # Display as percentages (0-100) color_scheme="viridis", # Colormap name color_scale="log", # Logarithmic color scale min_value=0.1, # Minimum value for color scale max_value=0.8, # Maximum value for color scale n_labels=15, # Number of tick labels tick_fontsize=10, # Font size for tick labels label_fontsize=14, # Font size for axis labels square=False, # Non-square cells annotate=True, # Annotate cells with values)Custom Title Generation
Section titled “Custom Title Generation”You can provide a custom title string or use a callback function:
# Using a string titledata.plot(title="My Custom Title")
# Using a callback functiondef title_callback(data_df, results_df): n_total = results_df.groupby("delay").total.first().iloc[0] return f"Detectability Analysis (n={n_total} sources)"
data.plot(title_callback=title_callback)Working with Custom Column Names
Section titled “Working with Custom Column Names”If your lookup table uses different column names, specify them when creating the LookupData object:
# Table with custom column namesdata = LookupData( "my_lookup_table.parquet", delay_column="delay_col", # Custom delay column name obs_time_column="time_col", # Custom observation time column name)
# Filtering and plotting work the same waydata.set_filters(("event_id", "==", 1))data.plot(title="Custom Columns Example")Advanced Examples
Section titled “Advanced Examples”Filtered Analysis
Section titled “Filtered Analysis”Analyze detectability for specific subsets of your data:
# Filter for south site, low zenith, specific eventsdata.set_filters( ("irf_site", "==", "south"), ("irf_zenith", "<=", 40),)
data.set_observation_times(np.logspace(1, np.log10(7200), 10, dtype=int))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 8))data.plot( ax=ax, title="Detectability: South Site, Low Zenith, Events 1-3", max_exposure=2, as_percent=True, color_scheme="viridis", return_ax=True,)plt.tight_layout()plt.savefig("filtered_detectability.png", dpi=150, bbox_inches="tight")plt.close()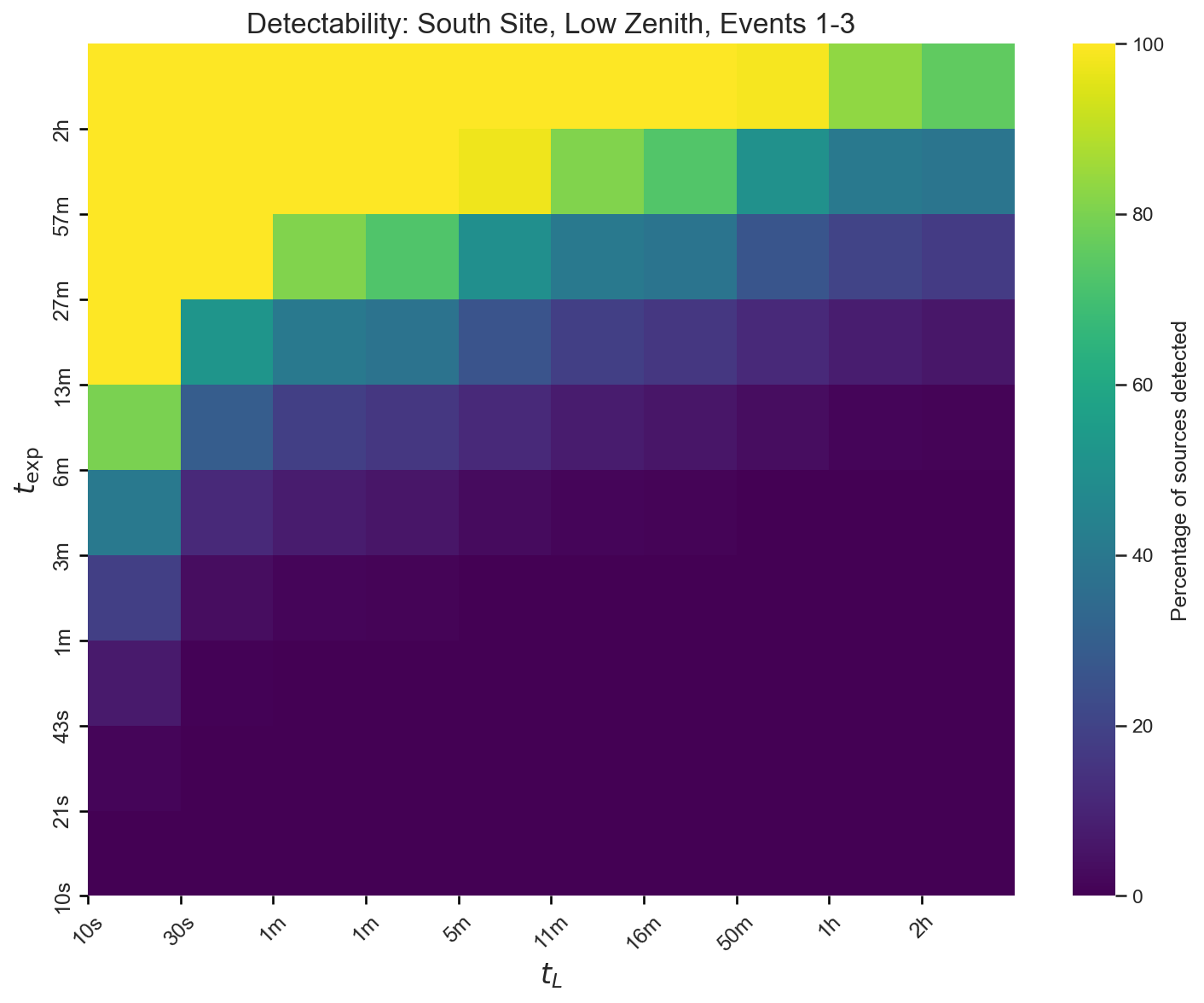
Grid of Heatmaps
Section titled “Grid of Heatmaps”Compare multiple configurations side-by-side using create_heatmap_grid():
from sensipy.detectability import create_heatmap_grid
# Create multiple LookupData objects with different filtersdata_north_z20 = LookupData(lookup_path)data_north_z20.set_filters(("irf_site", "==", "north"), ("irf_zenith", "==", 20))
data_north_z40 = LookupData(lookup_path)data_north_z40.set_filters(("irf_site", "==", "north"), ("irf_zenith", "==", 40))
data_south_z20 = LookupData(lookup_path)data_south_z20.set_filters(("irf_site", "==", "south"), ("irf_zenith", "==", 20))
data_south_z40 = LookupData(lookup_path)data_south_z40.set_filters(("irf_site", "==", "south"), ("irf_zenith", "==", 40))
# Create a 2x2 gridfig, axes = create_heatmap_grid( [data_north_z20, data_north_z40, data_south_z20, data_south_z40], grid_size=(2, 2), max_exposure=1, title="Detectability Comparison: Site and Zenith Configurations", subtitles=[ "North, z20", "North, z40", "South, z20", "South, z40", ], cmap="mako",)plt.savefig("detectability_grid.png", dpi=150, bbox_inches="tight")plt.close()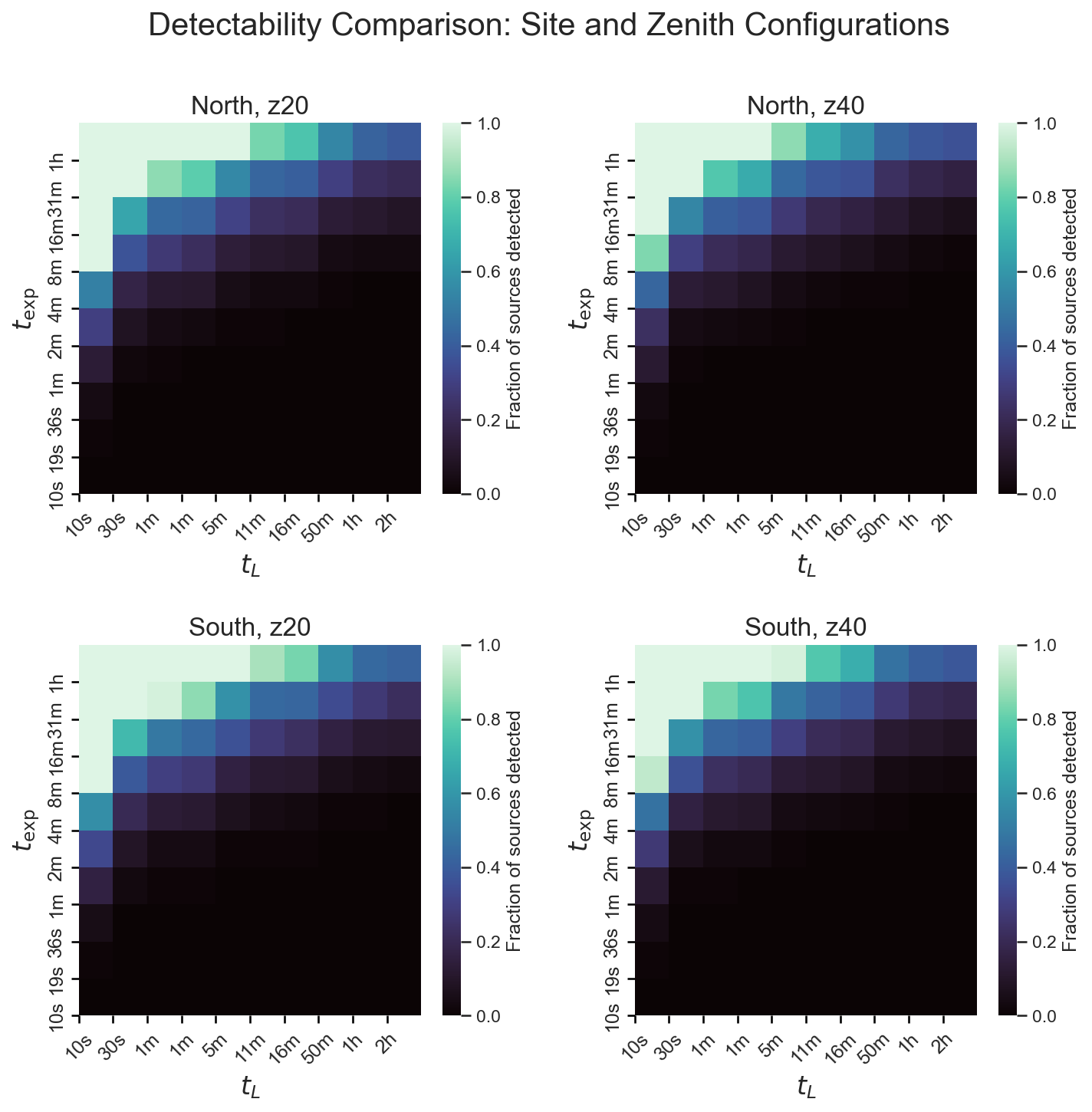
Accessing Results Data
Section titled “Accessing Results Data”You can access the calculated detectability results programmatically:
# Calculate resultsdata.set_observation_times([10, 100, 1000, 10000])results = data.results
print(results.columns)# ['delay', 'obs_time', 'n_seen', 'total', 'percent_seen']
# Filter results for specific delaydelay_1000 = results[results["delay"] == 1000]print(delay_1000[["obs_time", "percent_seen"]])Resetting Filters
Section titled “Resetting Filters”Reset filters to return to the full dataset:
# Apply filtersdata.set_filters(("irf_site", "==", "north"))
# Reset to full datasetdata.reset()Data Requirements
Section titled “Data Requirements”Your lookup table must contain at least two columns:
- Delay column (default:
obs_delay): Observation delay times in seconds - Observation time column (default:
obs_time): Required observation times in seconds (negative values indicate non-detection)
Additional metadata columns are optional but useful for filtering:
event_id: Event identifierirf_site: Observatory site ("north"or"south")irf_zenith: Zenith angle in degreesirf_ebl_model: EBL model name- Any other columns you want to filter by